|
Chapter 7 : Early Defibrillation And Using An AEDDefibrillation may be the only treatment to restore normal heart activity and save someone's life if they go into cardiac arrest. The AED has built-in voice prompts to guide the user in a simple and clear manner. Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) and pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) are examples of fatal and irregular rhythms that can be corrected by the use of an AED. These are discussed in the next chapter. Early Defibrillation And Using An AED Video:BLS survey is used for all cardiac arrest patients:
Why is Defibrillation Important?In a situation where the patient is in cardiac arrest and the rhythm is VF or pulseless VT, defibrillation is the only treatment. Defibrillation stops the arrhythmias from continuing and assists in obtaining normal heart rhythm. ALWAYS REMEMBER DEFIBRILLATION DOES NOT RESTART THE HEART! It “shocks” the heart with electrical impulses. IMPORTANT: IMMEDIATELY RESUME CPR AFTER DEFIBRILLATION! Most common rhythms seen in sudden cardiac arrest are VF and pulseless VT and for that reason early defibrillation is very important. Steps used to operate AEDsAEDs may have different models and manufactures, but most of them can be used by using the following steps:
Learning Outcomes:You have completed Chapter VII. Now you should be able to:
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Defibrillation may be the only treatment to restore normal heart activity and save someone's life if they go into cardiac arrest. The AED has built-in voice prompts to guide the user in a simple and clear manner. Ventricular Fibrillation (VF) and pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia (VT) are examples of fatal and irregular rhythms that can be corrected by the use of an AED. These are discussed in the next chapter.
| STEPS | ASSESSMENT | TECHNIQUE/ACTION | |
| 1 | Check for response |
|
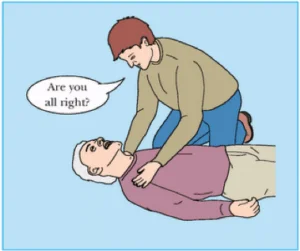 |
| 2 | Activate the emergency response system and get AED |
|
 |
| 3 | Circulation |
|
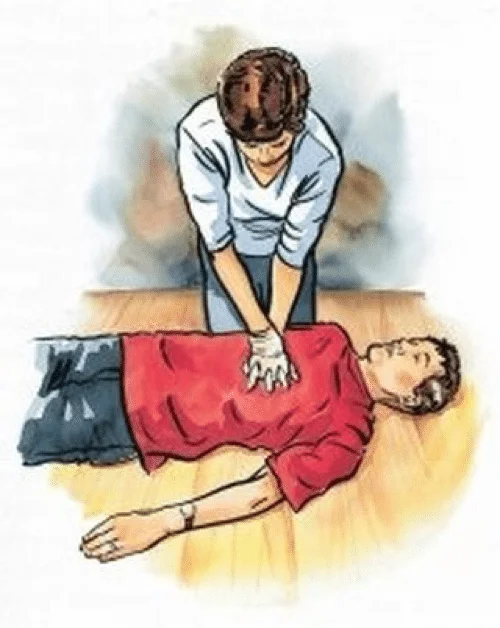 |
| 4 | Defibrillation |
|
 |
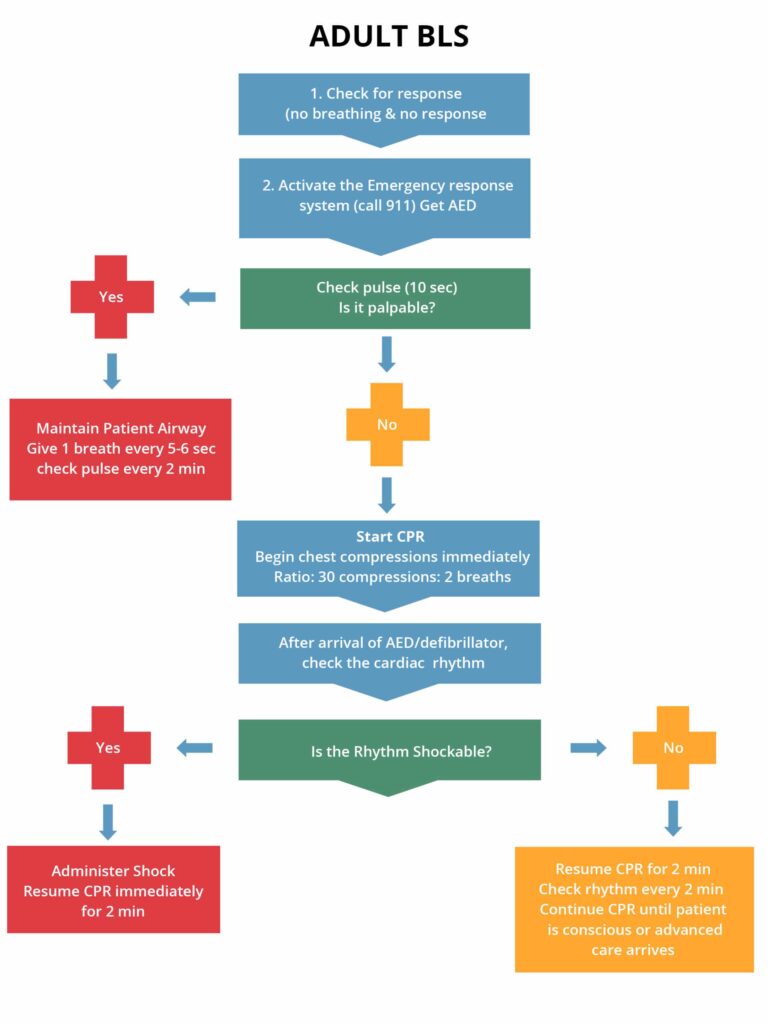
In a situation where the patient is in cardiac arrest and the rhythm is VF or pulseless VT, defibrillation is the only treatment. Defibrillation stops the arrhythmias from continuing and assists in obtaining normal heart rhythm. ALWAYS REMEMBER DEFIBRILLATION DOES NOT RESTART THE HEART! It “shocks” the heart with electrical impulses. IMPORTANT: IMMEDIATELY RESUME CPR AFTER DEFIBRILLATION! Most common rhythms seen in sudden cardiac arrest are VF and pulseless VT and for that reason early defibrillation is very important.
AEDs may have different models and manufactures, but most of them can be used by using the following steps:
| Step | Action |
| 1 | Turn on the AED |
| 2 |
Put the electrode pads to the patient’s bare chest
|
| 3 |
Analyze the rhythm
|
| 4 |
If shock is needed, CLEAR THE PATIENT
|
| 5 |
Continue CPR beginning with chest compressions
|

You have completed Chapter VII. Now you should be able to: